When applying for a mortgage, one of the most important factors lenders consider is your mortgage to income ratio — more commonly known as your debt-to-income (DTI) ratio . This number helps lenders determine whether you can afford the monthly payments on a home.
In this post, we’ll explain:
- What the mortgage to income ratio means
- How it affects your ability to get approved
- What’s considered a good DTI
- How to calculate your own ratio
Let’s dive in.
What Is the Mortgage to Income Ratio?
Your mortgage to income ratio , or debt-to-income ratio (DTI) , is the percentage of your gross monthly income that goes toward monthly debt payments , including:
- Mortgage payment (principal + interest)
- Property taxes
- Homeowners insurance
- HOA fees (if applicable)
- Other recurring debts (e.g., car loans, student loans, credit card minimums)
📊 Lenders use this ratio to assess your financial health and ability to manage a mortgage.
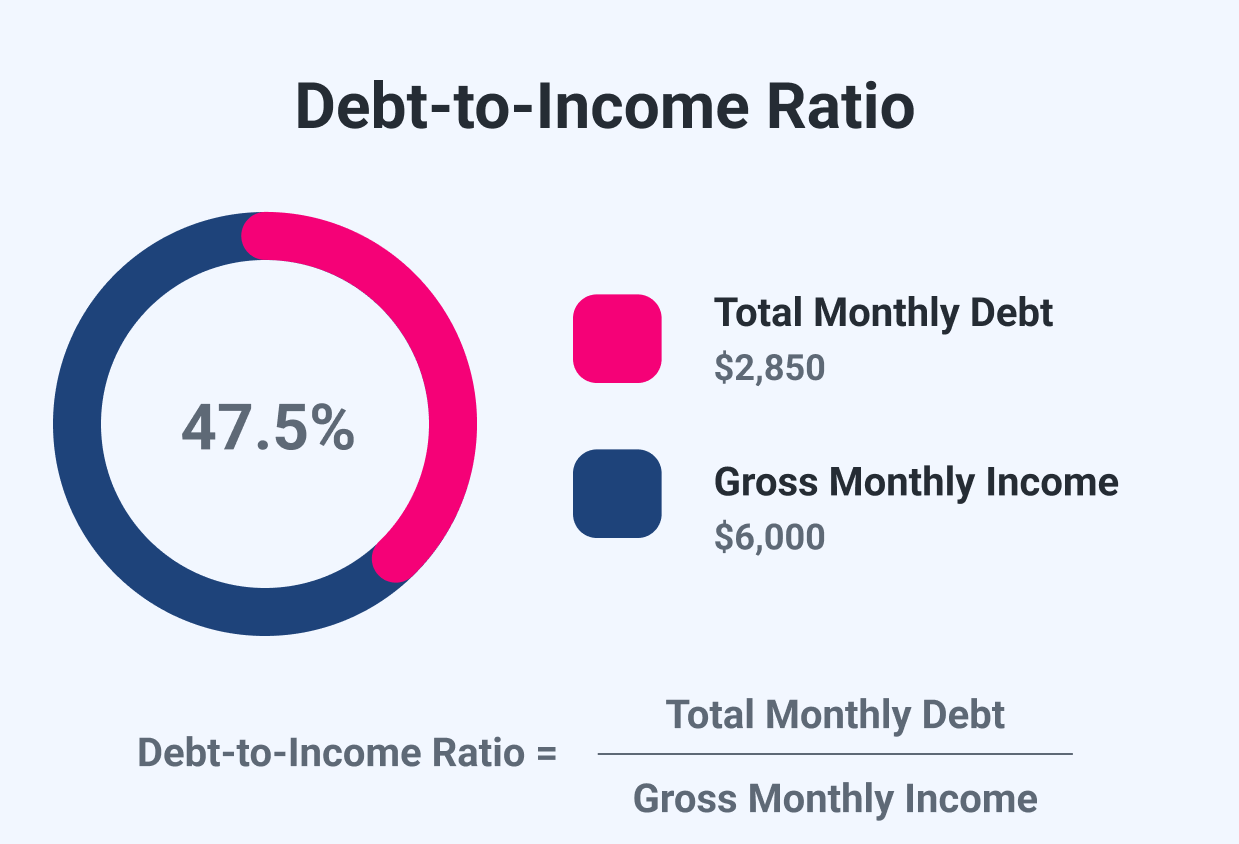
How to Calculate Your Mortgage to Income Ratio
Use this simple formula:
1DTI = (Total Monthly Debt Payments ÷ Gross Monthly Income) × 100
Example:
- Monthly mortgage payment: $1,800
- Car loan: $300
- Student loan: $200
- Total debt: $2,300
- Gross income: $7,000/month
1DTI = ($2,300 ÷ $7,000) × 100 = 32.9%
This DTI is within the acceptable range for most lenders.
What Is a Good Mortgage to Income Ratio?
Most lenders prefer:
| Below 36% | Ideal – strong chance of approval |
| 36% – 41% | Acceptable – may still qualify |
| 42% – 49% | High – may require higher down payment or better credit |
| 50% or above | Risky – harder to qualify unless other factors are strong |
✅ General Rule : Most lenders want your housing payment (PITI) to be no more than 28% of your gross income , and total debt under 36–43% .
Why Does Mortgage to Income Ratio Matter?
Lenders use the mortgage to income ratio to evaluate:
- Whether you can comfortably afford the new mortgage
- Your risk level as a borrower
- The maximum mortgage amount you qualify for
Even if you have a great credit score and a large down payment, a high DTI can still hurt your chances of approval.
How to Improve Your Mortgage to Income Ratio
Here are some ways to lower your DTI before applying:
1. Pay Off Debt
Focus on reducing balances on credit cards, auto loans, or student loans.
2. Avoid New Debt
Don’t take on new loans or credit lines before applying for a mortgage.
3. Increase Income
Consider side jobs, freelance work, or asking for a raise to boost your gross income.
4. Delay Major Purchases
Wait until after closing on your home before buying big-ticket items like furniture or appliances on credit.
Sample Mortgage Affordability Based on Income
| $4,000 | $1,120 | ~$170,000 |
| $5,000 | $1,400 | ~$210,000 |
| $6,000 | $1,680 | ~$250,000 |
| $7,000 | $1,960 | ~$290,000 |
| $8,000 | $2,240 | ~$330,000 |
(Note: These are rough estimates and do not include taxes, insurance, or PMI.)
Final Thoughts
Understanding your house mortgage to income ratio is key to knowing how much house you can afford and whether you’ll qualify for a loan. A healthy DTI gives you more flexibility, better rates, and greater confidence when making an offer on a home.
Before applying for a mortgage, calculate your DTI, pay down debt if needed, and talk to a lender to understand your budget.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What is the ideal mortgage to income ratio?
Most lenders prefer a DTI below 36% , with no more than 28% going toward housing costs.
Q2: Can I get a mortgage with a DTI over 50%?
It’s possible but challenging — you may need a larger down payment, excellent credit, or special loan programs.
Q3: Does DTI affect mortgage interest rates?
Yes — borrowers with lower DTIs often qualify for better interest rates and loan terms.
Join The Discussion